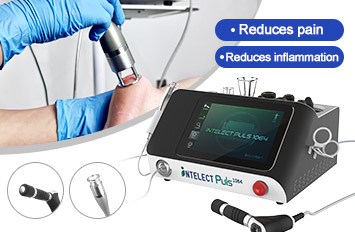
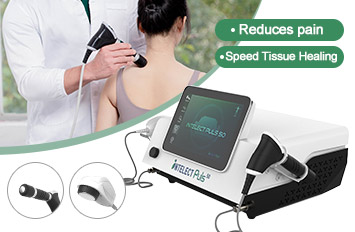
Working Principle
A shock wave is defined as a wave with a rapid increase of increase of pressure within a very short time and then having a gradual decrease of pressure with a small negative pressure phase. Shock wave is aimed at the affected area that are the source of chronic pain, the influence of the shock waves causes to the dissolution of calcium deposits and leads to better vascularization. The after-effect is relief from the pain.
Shock wave has the following effects:
Cellular: Increase in cell membrane transmittance by improving ionic channels activity, stimulation of cell division, stimulation of cellular cytokines production.
Reproduction of vessels in the area of tendons and muscles: Improvement of blood circulation, increase in concentration of growth factor beta1, chemotactic, and mitogenic effect on osteoblasts.
Effect on nitrogen oxide system: Bone healing and remodeling.
Improvement of micro-circulation and metabolism.
Dissolution of calcified fibroblasts.
supports the production of collagen.
Reduction in tissue tension
Analgesic effect.
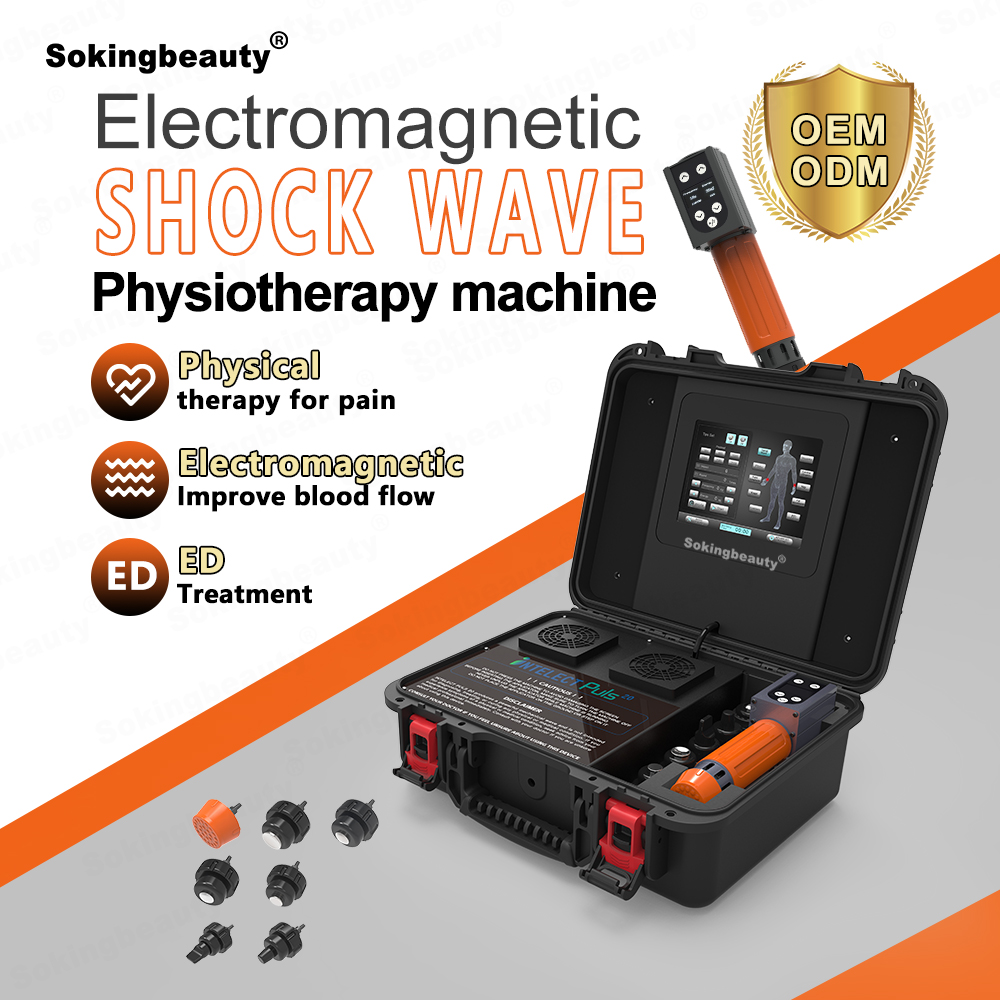



.jpg)



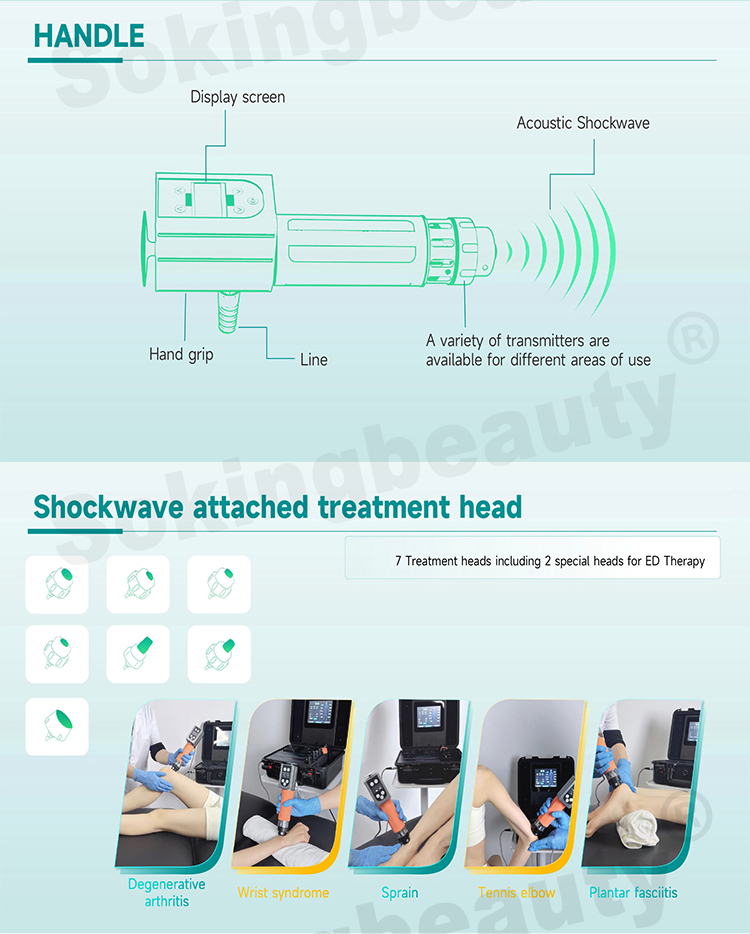







.jpg)